module Button = {
@react.component
let make = (~count) => {
let times = switch count {
| 1 => "once"
| 2 => "twice"
| n => n->Int.toString ++ " times"
}
let text = `Click me ${times}`
<button> {text->React.string} </button>
}
}import * as JsxRuntime from "react/jsx-runtime";
function Playground$Button(props) {
var count = props.count;
var times = count !== 1 ? (
count !== 2 ? count.toString() + " times" : "twice"
) : "once";
var text = "Click me " + times;
return JsxRuntime.jsx("button", {
children: text
});
}
var Button = {
make: Playground$Button
};
export {
Button,
}
Leverage the full power of JavaScript in a robustly typed language without the fear of `any` types.
ReScript is used to ship and maintain mission-critical products with good UI and UX.
Quick Install
The fastest build system on the web
ReScript cares about a consistent and fast feedback loop for any codebase size. Refactor code, pull complex changes, or switch to feature branches as you please. No sluggish CI builds, stale caches, wrong type hints, or memory hungry language servers that slow you down.
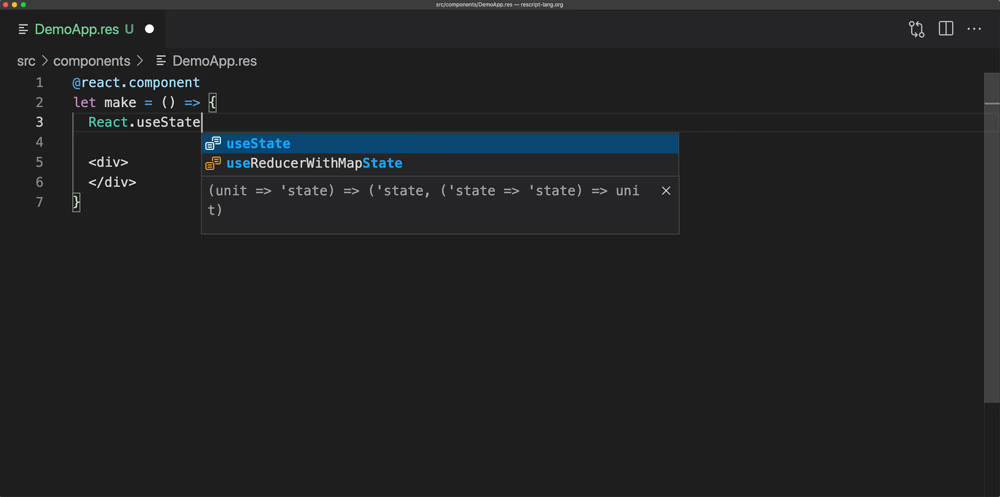
Type Better
The familiar JS ecosystem at your fingertips

A community of programmers who value getting things done
No language can be popular without a solid community. A great type system isn't useful if library authors abuse it. Performance doesn't show if all the libraries are slow. Join the ReScript community — A group of companies and individuals who deeply care about simplicity, speed and practicality.
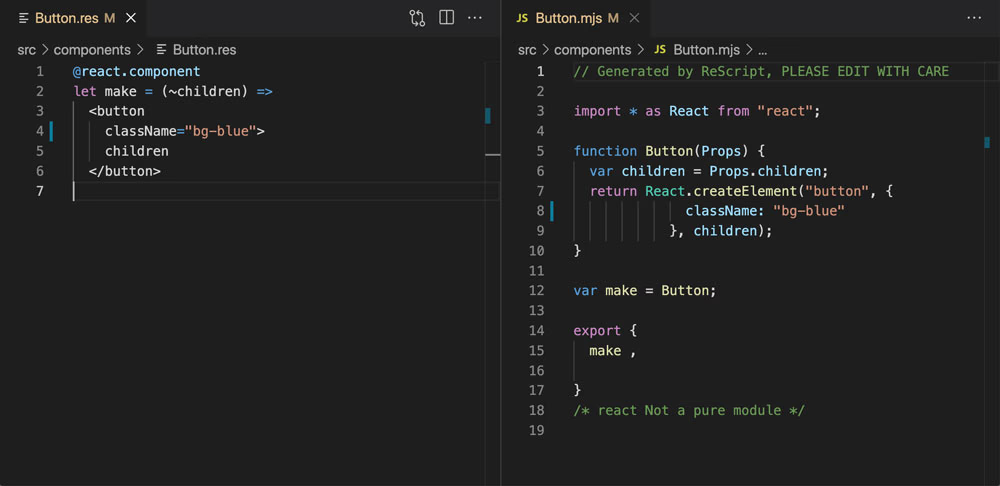
Tooling that just works out of the box
A builtin pretty printer, memory friendly VSCode & Vim plugins, a stable type system and compiler that doesn't require lots of extra configuration. ReScript brings all the tools you need to build reliable JavaScript, Node and ReactJS applications.
Easy to adopt — without any lock-in
ReScript was made with gradual adoption in mind. If you ever want to go back to plain JavaScript, just remove all source files and keep its clean JavaScript output. Tell your coworkers that your project will keep functioning with or without ReScript!
Trusted by our users
Curated resources

Language Manual

ReScript + React

Gradually Adopt ReScript

